| In the
Services for Sharing Your Drawings and
Autodesk Streamline articles, I reviewed various Autodesk services
(My Files, Autodesk ProjectPoint™, and Autodesk Streamline™) that help
you manage, track, secure, and share electronic design data over the
Internet and via e-mail. In this article, we're going to look at the
different software features and data formats Autodesk has developed that
make this sort of design sharing easier.
Through features
such as eTransmit, ePlot, and DesignXML, you can share your drawings in
the way that best meets your needs. Use eTransmit to easily bundle
multiple files into a single package that's convenient for sending
electronically. With ePlot, create an electronic plot of your drawing
that mimics its paper alternative and send that out for review rather
than the paper-based drawings. Through DesignXML, a design data schema
for representing DWG drawing data in XML (Extended Markup Language)
channels share specific design data with any CAD application.
Packaging Files
with eTransmit
The
eTransmit feature is specifically designed to address the challenges
of electronically sharing drawings with others over e-mail or web
posting. For example, it automatically ensures that all files associated
with a drawing, including xrefs and fonts, are included with the set of
files (called a transmittal set) that you are preparing to share
electronically (see Figure 1). This method guarantees that the recipient
will have all the files required to open and edit the drawing.
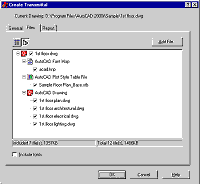
Figure 1: eTransmit automatically adds all support files to the
transmittal set.
(click image to enlarge)
eTransmit also
helps you track who has received what set of drawings. It automatically
generates a report detailing the files included in the transmittal set.
And you can add custom notes to the report, including whom you plan to
send the files to and where these people are located. You can then post
the transmittal set to your Intranet/Extranet, or send a copy as an
e-mail attachment and save the the original transmittal set in your
project directory.
Introduced in
AutoCAD® 2000i, eTransmit is enhanced in AutoCAD 2002 to automatically
include a copy of an AutoCAD Drawing Standards (DWS) Check File if one
is associated with the drawing. DWS Check Files are associated with
specific drawings and are used to verify that various drawing elements,
such as layers and text styles, comply with the designated standard
format (see
Maintaining AutoCAD Drawing Standards by Dave Pitzer for a
description of the STANDARDS command).
Creating
Electronic Plots with ePlot (and DWF)
With the AutoCAD
ePlot feature, you can create very compact electronic plots of
drawings and share those electronically rather than the actual paper
drawings. Just attach your ePlots to e-mails or post them to your
Intranet/Extranet. E-mail recipients or web visitors can easily view
them using a free viewer that plots the files to local system printers.
With ePlot you are creating web-enabled, plot-ready electronic copies of
your drawings.
When you use ePlot
to create electronic plots of your drawings, you're actually creating
DWF (Drawing Web Format) files. These small, compact files produce
high-quality images specifically designed to quickly display over the
Internet. While DWFs have been around for a while, the updated version
in AutoCAD 2002 includes enhancements with which you can produce DWFs
optimized either for accurate plotting or for viewing without the need
for AutoCAD software. And despite their compactness, DWFs contain the
same level of detail and quality as a plot generated from AutoCAD
software.
To complement the
updated DWF format, Autodesk enhanced both
Volo® View and
Volo View Express. These two viewers provide many features,
including Zoom and Pan, Layer On/Off control, and a set of markup tools
for redlining and adding comments to DWFs. Volo View Express is a free
download, while Volo View includes several additional features and may
be purchased online.
Sharing Design
Data with DesignXML
DesignXML represents the first step in Autodesk's move toward
presenting DWG drawing data in XML (Extended Markup Language) format.
With XML, an open meta-markup language designed for preparing content
for posting to the Internet, authors, developers, and content providers
can define specific languages for specific domains—such as design, in
the case of AutoCAD. XML is already widely used and accepted. So look at
DesignXML as the "web-aware" replacement for DXF (Drawing Exchange
Format) files. There are many tools available that work with XML and
many more programmers are familiar with XML than with the DXF format.
AutoCAD 2002 writes and reads XML files that conform to the emerging
Design XML and AcDbXML schema definitions. Figure 2 shows a portion of
an AutoCAD DesignXML output file that other CAD systems as well as
non-CAD applications can easily read.

Figure 2: A portion of an AutoCAD 2002 drawing's output to DesignXML
format.
AutoCAD 2002
supports DesignXML in two ways:
1. You can save
any or all objects in a drawing to DesignXML format using the WBLOCK
command and manually giving the file an XML extension in the file name
box of the Write Block dialog box.
2. You can insert
a DesignXML format file much as you would a standard DWG file using the
INSERT command. In the Select Drawing File dialog box, set the Files of
type list box to filter for XML file extensions.
You can find out
more about DesignXML from the following two articles:
1.
Creating and
loading DesignXML files
2.
The
Importance of DesignXML
Summary
Autodesk has developed software features and data formats that make it
easy to share your design data electronically in the format and
communications channel that work best for you. Whether you are quickly
bundling a drawing and all its support files into a single electronic
package, creating paperless electronic plots of drawings, or using the
power of the DesignXML language, you have a variety of convenient and
useful methods for sharing your designs.
|

