Laboratory.Ru
List of Papars on Science
& Engineering
Jury Dmitrievich Batalin
4761, Visaginas, Lietuva (Lithuania), Visagino
11-14,
home tel.: +3706632609, work tel.: +3706629096, batalin@tts.lt
Keywords: internal irradiation, doze, model of transferring, radionuclide, tritium, nuclear hazardous enterprise. ecology, radiating safety
|
Laboratory.Ru |
|
|
Model of transferring radionuclides into
the environment from nuclear hazardous enterprises.
Jury Dmitrievich Batalin 4761, Visaginas, Lietuva (Lithuania), Visagino
11-14, |
One more way of transferring radionuclides to the environment from nuclear hazardous enterprises has been considered. Workers of these enterprises carry out the transferring. In the greater measure, the unreasonable receipt of radionuclides occurs in an organism of members of the professional worker family and in smaller measure in environmental him people. The transferring of hydrogen - tritium radionuclide as special case have been considered.
The irradiation of the population by industrial sources is limited to by maintenance [2]:
Any nuclear hazardous enterprises working or stopped operation represents potential radiating danger, both to the population, and to an environment. The basic ways of transferring radionuclides outside nuclear hazardous enterprises are following:
In all these cases the overdraft of the nuclides output from the enterprises to the environment in various ways can result in an irradiation of the population, finally. These ways of transferring radionuclides are considered in [3].
However, the main question is whether all ways of transferring radionuclides into the environment from nuclear hazardous enterprises are enough full designated? The analysis of professional work of nuclear hazardous enterprises personnel have shown, that exists as a minimum one more way of transfer.
Such way is way of transferring radionuclides from nuclear hazardous enterprises into the environment by personnel of these enterprises.
During a working shift, the personnel of the enterprises absorbs radionuclides contained in the atmospheric air. The organism of professional worker accumulate the radionuclides. Confirmations of it are results of measurements of radionuclides concentration in organism of workers on installations of " System of measurement of the person. It means, that the worker would not apply means of protection. It is impossible to exclude the receipt of nuclides in organism completely.
The external contamination of the worker body usually removes after passage sanitary point, while it is obviously impossible to remove the internal contamination.
The internal irradiation of the population can be estimated, if concentration nuclides in atmospheric air are known. Background value of industrial nuclides concentration in atmospheric air of the settlements located near the nuclear enterprises differ in a small degree from values of the global atmosphere pollution and have limits (1?5) *10-6 Bk/m3. Measurement of such small concentrations is connected to the certain technical difficulties.
What would concentration nuclides in atmospheric air, their receipt in the organism of the person and a loss from organism, is defined:
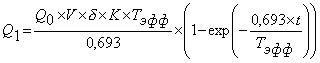 , Bk;
(1)
, Bk;
(1)
Where:
Q1 - concentration of nuclide in organizm of person after t hours, Bk.
Q0 - the mean of nuclide concentration in the atmospheric air , Bk/m3.
V - volume of air inhaling by a person per 1 hour, m3/hour.
![]() v the coefficient of a
delay radionuclide in the organism after a breath of atmospheric air.
v the coefficient of a
delay radionuclide in the organism after a breath of atmospheric air.
K - the coefficient that takes into account the nuclide receipt through a skin.
Teff - the effective period of nuclide half-removing from organism, hour.
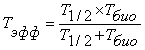 , Hour;
(2)
, Hour;
(2)
Where:
T1/2 - half-time period of a nuclide, hour;
Tbio - the biological half-removing period of a nuclide from organism, hour.
As follows from equation (2), accumulation of a nuclide in organism essentially depends from relation of T1/2 and Tbio.
At Tbio> > T1/2 the considered nuclide will remove from organism with the period which equals to a half-time period.
At Tbio = T1/2 the removing of the nuclide will equal 0,5 Tbio or 0,5 T1/2.
At Tbio< < T1/2 the removing of the nuclide will equal Tbio.
Another important factor which is necessary to take into account at calculation of accumulation nuclide in organism, it is change in time of inhaled concentration nuclide.
If during one year value of nuclide concentration in atmospheric air remain practically constant its saturation in an organism will come approximately through 5 - 6 Teff.
In another case if daily concentration will change over a wide range then function of accumulation will have more complex character. Then the concentration can be determined by numerical integration.
Besides the inhalation way of receipt nuclide in an organism of the person exists still peronal way. It is receipt of nuclides with food and water. Nevertheless, the result of influence of nuclide radiation is the same - the nuclides extend the harmful influence on all bodies and fabrics of organism. During only one day the activity of the nuclide which income into the environment will equal:
![]() , Bk;
(3)
, Bk;
(3)
where:
Q1 - the activity of the nuclide, which will accumulate in organism of worker after t hours, at his presence in industrial room, Bk
Q2 - the activity of the nuclide, which will remove from organism at presence of worker outside of industrial room after t2 hours, Bk
Q3 - the activity which will stay in organism of worker before start the new working shift , Bk
The circuit of model of transferring radionuclides outside of the nuclear enterprise by the professional worker is submitted on Fig1.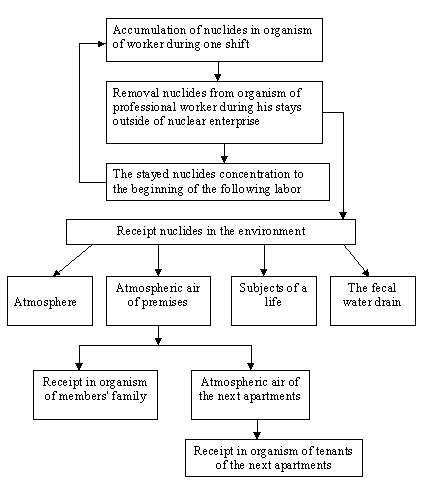
Such model of transfer equally concerns both to solid radionuclides, and to gaseous.
The mechanism of removal nuclides from organism has complex character, nevertheless, all of them get in inhabitancy of the professional worker.
Removing nuclides from organism occurs with exhaled air, excrements, through sweat-glands, tears, bleedings and etc.
The most part of time the professional worker stays in the living quarters and also some time - in places of public using. Therefore the removing nuclides will be traveled from the organism of the worker into the atmospheric air and water environments and further in organism of members of his family, objects of household and etc.
The special place in ?Model of transferring radionuclides into the environment from nuclear hazardous enterprises¦ occupies radionuclide tritium. The degree of tritium transfers into the person, members of the professional worker family, is more in order than transfer of solid radionuclides (Cs-137, Co-60 etc.). It is explained by its unique physical properties.
The calculations which have been carried out according to "Model-" showed, that at concentration of tritium in atmospheric air of an industrial rooms of the nuclear enterprise equal 40 Bk/m3, approximately in 50 days (at five-day working week) in all body of the professional worker will be established equilibrium tritium concentration 8000 Bk on all body, in atmospheric air of his apartment 2,7 Bk/m3, in an organism of his child is 400 Bk on all body.
On Fig. 2,3 are shown diagrams of tritium accumulation in organism of the professional worker and his child.
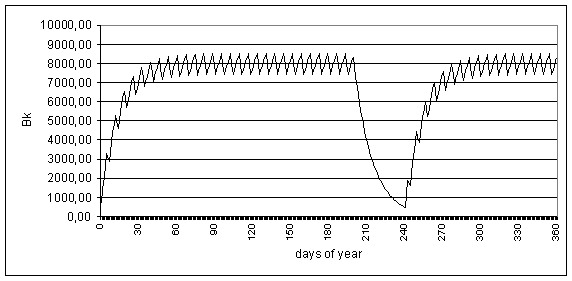
Fig. 2. Tritium accumulation in organism of the worker in view of the next holiday by duration of 40 days
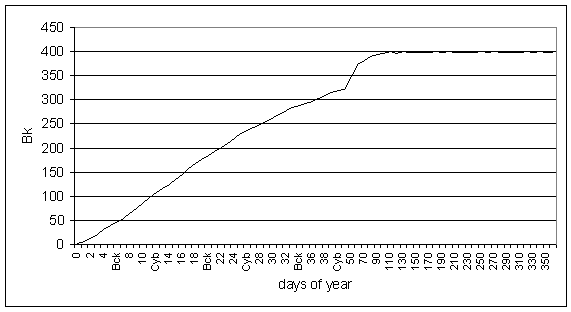 Fig. 3. Tritium accumulation in an organism of the child
in the age of 1-2 years
Fig. 3. Tritium accumulation in an organism of the child
in the age of 1-2 years
According to work [4] the average tritium concentration in the adult person is 2,8 Bk on all body. It turns out, that in a body of the professional worker of the nuclear enterprise this value will be exceeded in 3000 times, and for the child in 800 times (taking into account weight of his body).
In connection with considered ?Model ..¦ there is a question:
?What is the degree of risk for the person which is not connected with nuclear manufacture, but only living near to it? ¦. It is evidently possible to answer that such risk exists. And the degree of it is more for members of family of the professional worker and less for other population.
Till now this way of transfer is not considered in any regulatory documents on radiation protection of population. Nevertheless, such way exists and existed from the moment of the beginning of nuclear technologies. Specificity of tritium measurement limits the large-scale measurements of his concentration however do not remove given question from the agenda. It also may concern such nuclides, as C-14, Sr-90.
As follows from ?Model -¦ the infringement of a principle deeply echeloned protection [1] which " is realized, first of all, takes place by creation of a series of barriers to which basically never and that should not threaten and which, in turn, should be broken before can damage to the person and to the environment " take place.
It is obvious that for reduction of uncontrollable till now radiation influence on the personnel of the nuclear enterprises and living near to their population, it is necessary the serious completion of existing technologies at these enterprises with the purpose of creation of reliable safety barriers. Besides it is quite possible, that some kinds of diseases of the person who has not been connected to nuclear manufacture, can be quite caused by such uncontrollable kind of a radiation irradiation. 25 partially genetically stipulated diseases (glaucoma, asthma, diabetes, cancer and etc.) which should be included into the population irradiation genetic risk assessment has been named by The UN Scientific Committee on the effects of atomic radiation (UNSCEA).
Moreover, UNSCEA defines tritium (H-3), carbon (C-14), chlorine (Cl-36), krypton (K2-85), iodine (J-129) as a environmentally and socially dangerous to man radionuclides.
The detailed validation of a considered way of transfer radionuclides into environment have been presented in the report ? Model of transferring radionuclides into environment from nuclear hazardous enterprises" in which the settlement formulas have been given, calculation of tritium accumulation in various objects have been made, the technique of measurement and selection have been described, the serviceability of ?Models ..¦ have been confirmed, the ways of tritium formation at the nuclear enterprises and its transition into atmospheric air of industrial premises have been considered.
?Model..¦ it is suitable for define potential of nuclear hazardous enterprises.

|
Laboratory.Ru |
For all questions You may contact us this way : mailto:info@laboratory.ru